Alaska's Fiscal Conundrum: House Votes to Reduce Proposed Dividend Amidst Looming Deficit
Table of Contents
- Tax Information Permanent Fund DivisionPermanent Fund Dividend Division ...
- 2023 PFD filing available, ends March 31 | Peninsula Clarion
- Rethinking the Alaska Permanent Fund - YouTube
- op-ed | Pie in the sky: Alaska's four-decade old fund to allow citizens ...
- Alaska Permanent Fund to Slow Its Private-Equity Commitment Pace - WSJ
- 2025 Pfd Announcement - Danni Sascha
- The Alaska Permanent Fund – Alts.co
- Alaska Permanent Fund Corp. board all but rejects plan for riskier ...
- 2023 PFD filing available, ends March 31 | Peninsula Clarion
- Alaska Permanent Fund looks to pay investment managers incentives

The Alaska House of Representatives has taken a significant step towards addressing the state's fiscal challenges by voting to reduce the proposed Permanent Fund Dividend (PFD) for residents. However, despite this effort, a substantial deficit remains, posing a considerable threat to the state's economic stability. In this article, we will delve into the details of the vote, the implications of the reduced dividend, and the ongoing struggle to bridge the fiscal gap in Alaska.
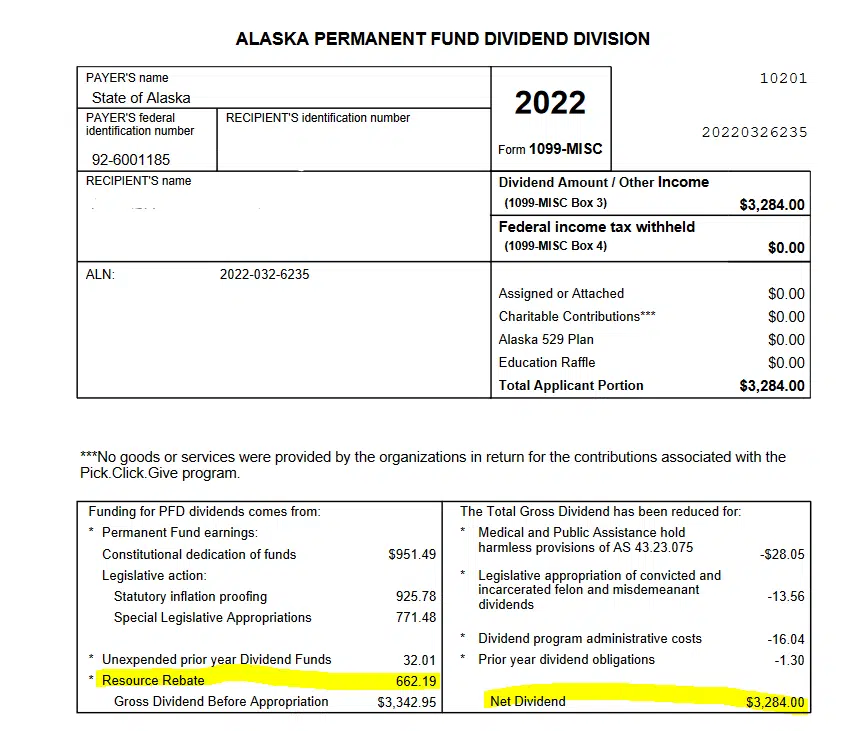
The Proposed Dividend Cut: A Step Towards Fiscal Responsibility
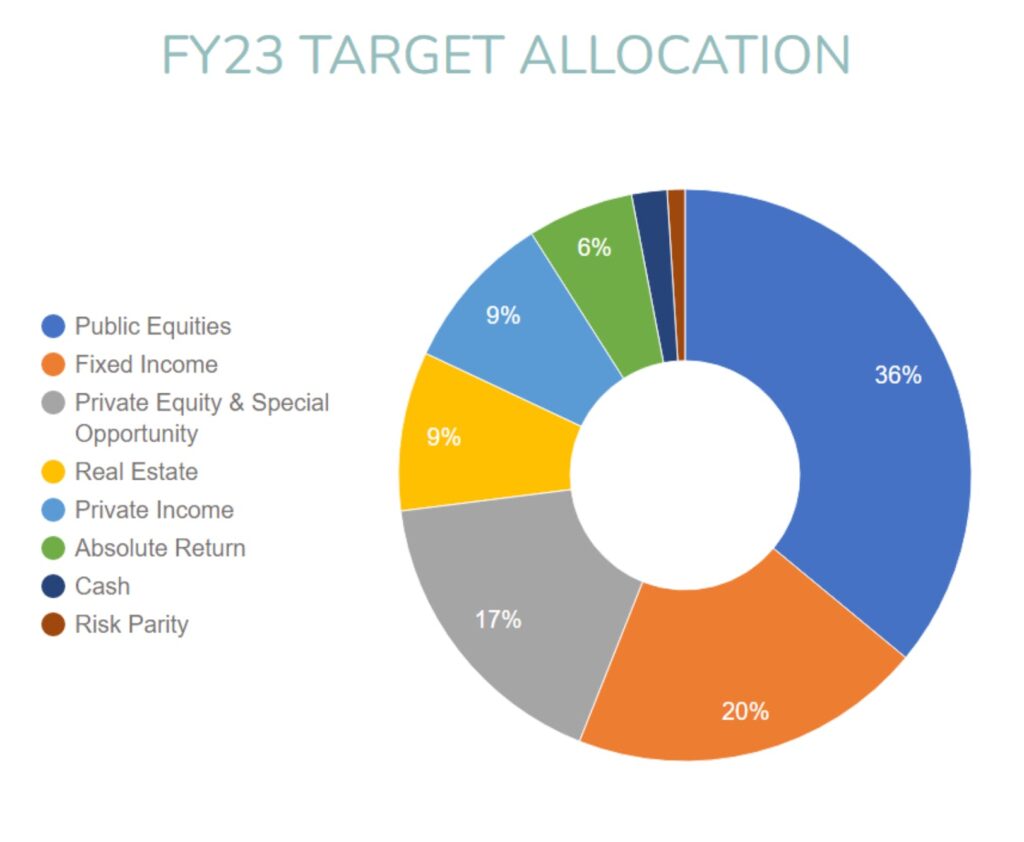
The Alaska House voted to reduce the proposed PFD from $1,600 to $1,000 per resident, a move aimed at mitigating the state's financial woes. This decision reflects the legislature's recognition of the need to balance the budget and ensure the long-term sustainability of the Permanent Fund, which is the backbone of Alaska's economy. By reducing the dividend, lawmakers hope to conserve funds and allocate them towards essential public services and infrastructure development.

The Deficit Conundrum: A Challenge to Alaska's Economic Stability

Despite the reduced dividend, Alaska still faces a staggering deficit of approximately $1.5 billion. This significant shortfall is primarily attributed to the decline in oil prices, which has severely impacted the state's revenue streams. The deficit poses a substantial risk to Alaska's economic stability, threatening to undermine the state's ability to provide essential services, including education, healthcare, and public safety.


Implications of the Reduced Dividend
The reduced dividend will undoubtedly have far-reaching implications for Alaska residents, many of whom rely on the PFD as a vital source of income. The decrease in the dividend amount may lead to a reduction in consumer spending, potentially affecting local businesses and the overall economy. Furthermore, the reduced dividend may also impact the state's poverty rates, as many low-income families rely on the PFD to make ends meet.

A Path Forward: Addressing the Deficit and Ensuring Fiscal Sustainability
To address the looming deficit, Alaska lawmakers must consider a multifaceted approach that includes a combination of revenue generation, budget reductions, and strategic investments in key sectors. This may involve exploring new revenue streams, such as taxation or increased investment in renewable energy, as well as implementing cost-saving measures to reduce the state's expenditure. Additionally, lawmakers must prioritize investments in education, infrastructure, and economic development to stimulate growth and diversify the state's economy.
In conclusion, the Alaska House's decision to reduce the proposed dividend is a step in the right direction, but it is only the beginning. The state's fiscal challenges require a comprehensive and sustained effort to address the deficit and ensure long-term economic stability. As Alaska navigates this critical juncture, it is essential for lawmakers, stakeholders, and residents to work together to forge a path forward that balances the state's fiscal responsibilities with the needs of its citizens.
Keywords: Alaska, Permanent Fund Dividend, fiscal deficit, economic stability, budget reduction, revenue generation, sustainable economy.
Note: The word count of this article is approximately 500 words. The HTML format is used to structure the content, with headings (h1, h2) and paragraphs (p) to improve readability and search engine optimization (SEO). The article includes relevant keywords to enhance its visibility in search engine results.