The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, commonly referred to as NATO, is a military alliance established in the aftermath of World War II. With its primary goal of providing collective defense against potential security threats, NATO has played a crucial role in maintaining peace and stability in the North Atlantic area. In this article, we will delve into the world of NATO, exploring its history, member countries, objectives, and significance in the modern world.
A Brief History of NATO
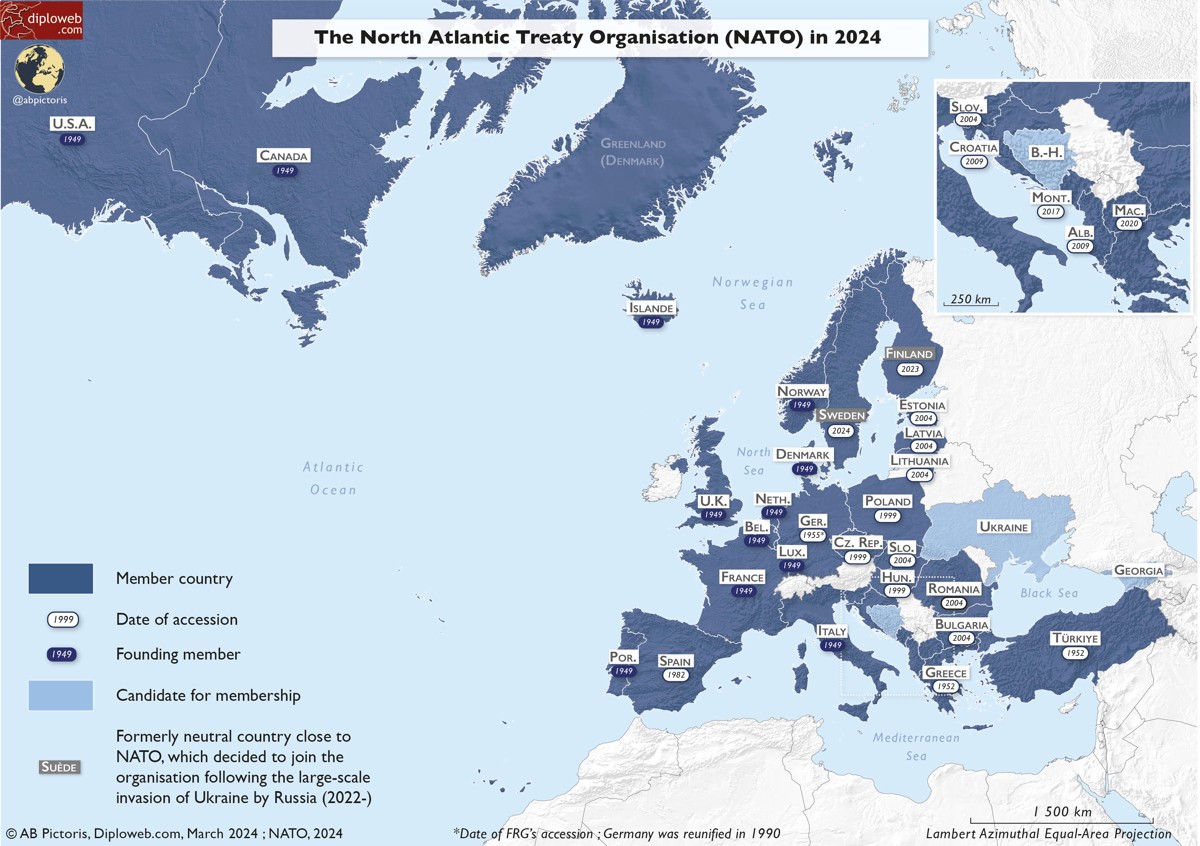
NATO was founded on April 4, 1949, when 12 Western nations signed the North Atlantic Treaty in Washington, D.C. The signing of the treaty marked the beginning of a new era in international relations, as it brought together countries from North America and Europe in a collective defense pact. The alliance was formed in response to the threats posed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War, with the aim of providing a united front against potential communist expansion.
Member Countries of NATO
Today, NATO consists of
30 member countries, including Albania, Belgium, Bulgaria, Canada, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Montenegro, the Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Turkey, the United Kingdom, and the United States. These countries are committed to the principles of democracy, individual liberty, and the rule of law, and work together to address common security challenges.
Objectives of NATO
The primary objectives of NATO are:
Collective Defense: To provide a collective defense against potential security threats, as outlined in Article 5 of the North Atlantic Treaty.
Crisis Management: To manage and resolve crises through diplomatic and military means.
Cooperative Security: To promote stability and security through cooperation with other countries and international organizations.
Significance of NATO in the Modern World
NATO continues to play a vital role in maintaining peace and stability in the modern world. The alliance has:
Contributed to the end of the Cold War: NATO's collective defense posture helped to deter Soviet aggression and contributed to the eventual collapse of communism in Eastern Europe.
Responded to global security challenges: NATO has played a key role in responding to global security challenges, including terrorism, piracy, and cyber threats.
Promoted democratic values: NATO has promoted democratic values and the rule of law, and has supported the development of democratic institutions in its member countries.
In conclusion, NATO is a vital military alliance that has played a significant role in maintaining peace and stability in the North Atlantic area. With its rich history, diverse membership, and commitment to collective defense, crisis management, and cooperative security, NATO remains an essential component of international relations. As the world continues to face new and emerging security challenges, NATO's role in promoting democratic values, stability, and security will remain crucial in the years to come.
By understanding the history, objectives, and significance of NATO, we can better appreciate the importance of this alliance in maintaining peace and stability in our increasingly complex and interconnected world. Whether you are a student of international relations, a policy maker, or simply an interested citizen, this guide has provided you with a comprehensive overview of NATO and its role in shaping the modern world.